Installation
Connect your serial adapter (usbcom1a works well if you don’t have one already) to the apu2c4 and start a program to use it, e.g. screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200. Then, power on the apu2c4 and configure it to do PXE boot:
- Press
F10to enter the boot menu - Press
3to enter setup - Press
nto enable network boot - Press
cto move mSATA to the top of the boot order - Press
eto move iPXE to the top of the boot order - Press
sto save configuration and exit
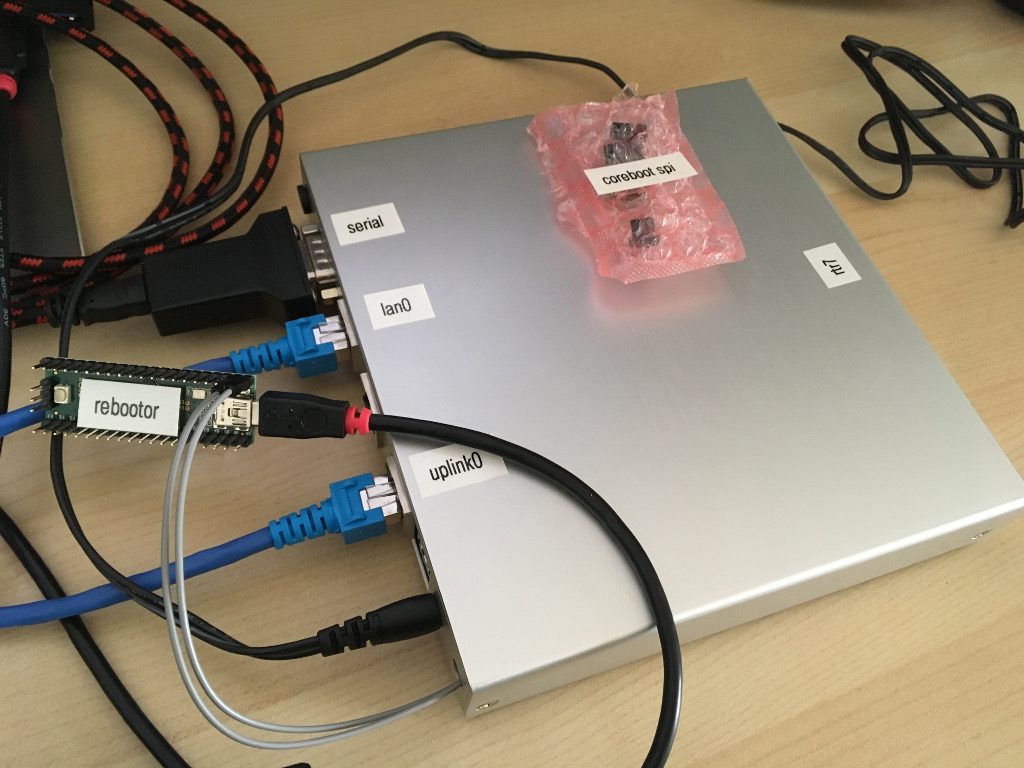
Connect a network cable on net0, the port closest to the serial console port:
Next, create a router7 gokrazy instance (see gokrazy quickstart if you’re unfamiliar with gokrazy):
go install github.com/gokrazy/tools/cmd/gok@main
go install github.com/rtr7/tools/cmd/...@latest
mkdir /tmp/recovery
gok -i router7 new
gok -i router7 edit
Change the config until you have the following fields set:
{
"Hostname": "router7",
"Packages": [
"github.com/gokrazy/fbstatus",
"github.com/gokrazy/hello",
"github.com/gokrazy/serial-busybox",
"github.com/gokrazy/breakglass"
"github.com/rtr7/router7/cmd/..."
],
"SerialConsole": "ttyS0,115200",
"GokrazyPackages": [
"github.com/gokrazy/gokrazy/cmd/ntp",
"github.com/gokrazy/gokrazy/cmd/randomd"
],
"KernelPackage": "github.com/rtr7/kernel",
"FirmwarePackage": "github.com/rtr7/kernel",
"EEPROMPackage": ""
}
Then, build an image:
GOARCH=amd64 gok -i router7 overwrite \
--boot /tmp/recovery/boot.img \
--mbr /tmp/recovery/mbr.img \
--root /tmp/recovery/root.img
And serve the image for netboot installation:
rtr7-recover \
--boot /tmp/recovery/boot.img \
--mbr /tmp/recovery/mbr.img \
--root /tmp/recovery/root.img
Specifically, rtr7-recover:
- trigger a reset if a Teensy with the rebootor firmware is attached
- serve a DHCP lease to all clients which request PXE boot (i.e., your apu2c4)
- serve via TFTP:
- the PXELINUX bootloader
- the router7 kernel
- an initrd archive containing the rtr7-recovery-init program and mke2fs
- serve via HTTP the boot and root images
- optionally serve via HTTP a backup.tar.gz image containing files for
/perm(e.g. for moving to new hardware, rolling back corrupted state, or recovering from a disk failure) - exit once the router successfully wrote the images to disk
Configuration
Interfaces
The /perm/interfaces.json configuration file will be automatically created if it is not present when you run the first recovery.
Example:
{
"interfaces": [
{
"hardware_addr": "12:34:56:78:9a:b0",
"name": "lan0",
"addr": "192.168.0.1/24"
},
{
"hardware_addr": "12:34:56:78:9a:b2",
"name": "uplink0"
}
]
}
Schema: see InterfaceConfig
Port Forwarding
The /perm/portforwardings.json configuration file can be created to define port forwarding rules.
Example:
{
"forwardings": [
{
"proto": "tcp",
"port": "22",
"dest_addr": "10.0.0.10",
"dest_port": "22"
},
{
"proto": "tcp",
"port": "80",
"dest_addr": "10.0.0.10",
"dest_port": "80"
}
]
}
Schema: see portForwardings
Updates
Run e.g. rtr7-safe-update -updates_dir=$HOME/router7/updates to:
- verify the router currently has connectivity, abort the update otherwise
- download a backup archive of
/perm - build a new image
- update the router
- wait until the router restored connectivity, roll back the update using
rtr7-recoverotherwise
The update step uses kexec to reduce the downtime to approximately 15 seconds.
Manual Recovery
Given rtr7-safe-update’s safeguards, manual recovery should rarely be required.
To manually roll back to an older image, invoke rtr7-safe-update via the
recover.bash script in the image directory underneath -updates_dir, e.g.:
% cd ~/router7/updates/2018-07-03T17:33:52+02:00
% ./recover.bash
Teensy rebootor
The cheap and widely-available Teensy++ USB development board comes with a firmware called rebootor, which is used by the teensy_loader_cli program to perform hard resets.
This setup can be used to programmatically reset the apu2c4 (from rtr7-recover) by connecting the Teensy++ to the apu2c4’s reset pins:
- connect the Teensy++’s
GNDpin to the apu2c4 J2’s pin 4 (GND) - connect the Teensy++’s
B7pin to the apu2c4 J2’s pin 5 (3.3V, resets when pulled toGND)
You can find a working rebootor firmware .hex file at https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/teensy_loader_cli/issues/38
Prometheus
See https://github.com/rtr7/router7/tree/master/contrib/prometheus for example configuration files, and install the router7 Grafana Dashboard.
© 2018 Michael Stapelberg and contributors